Website Owners Guide to Google Search Console
Updated 31 May 2021 (Published 16 July 2019) by Miles in Business Tips
Google Search Console is an absolute must. It tracks the performance of your website, and is vital for understanding how your website appears in their results. Let’s go through how it works, and how it can benefit Australian website owners.

Google Search Console provides valuable insights that help you understand what components of your website needs work. You want to address these, and optimise your website so it appears in Google search results.
Why would that matter? According to this report, Google accounts for a massive 95.11% market share of searches in Australia. The second most used search engine, Bing, sits at a lowly 3.49%. Google really has the market all sewn up.
If you don’t already have a Search Console account, don’t fret – I’ll explain how to sign up free.
If you already have a Google Search Console account, you can jump straight to Using Google Search Console.
How to create a Google Search Console account
To start using Google Search Console, you first need to create an account. There are two steps to this; creating the account and verifying ownership.
Your first step is visiting the Google Search Console website and clicking ‘Start now’.
When you are in Google Search Console, click on ‘+ Add property’ in the top left hand bar of any screen. This will then prompt you with two options as shown here.
You have the choice of adding a URL prefix property or Domain property.
Domain property
This is as stated; everything on a specific domain name, such as www.yourdomainname.com.au shop.yourdomainname.com.au etc. This is the most common setup. This also covers multiple protocols (http, https, ftp).
URL prefix property
This option includes only URLs with the specified prefix, including the protocol (http/https). For example, if you had a subdomain like shop.yourdomain.com.au or blog.yourdomain.com.au that you wanted to track separately than everything within yourdomain.com.au
Verifying website ownership
Google search console reveals some commercially sensitive data, so they are naturally strict about access. Before you can see any data, you need to verify you own the website. This step is easier than it sounds, and they give you a variety of ways to verify.
Google states that “Data should begin to appear in your property in a few days. Data collection for a property starts as soon anyone adds the property in any Search Console account, even before verification. Data collection continues as long as any user has that property in their account, whether or not it has a verified owner.”
You can be verified as the website owner using one of five different (and slightly technical) methods. These are;
- Upload a provided HTML file to your website (requires FTP access to your hosting provider)
- Add a specific HTML tag to your website (requires HTML editing access to your website)
- Make a change to your DNS records (required domain management access)
- Add Google Analytics code to your website
- Add a Google Tag Manager container snippet to your website
You can find out more about each of these steps, either in Google Search Console itself, or by reading this page on Search console help.
Using Google Search Console
Let’s go screen by screen, and explain what everything in Google Search Console represents. You may need to wait a few days from first signing up, to see much data in here.
There are a number of screens available to you within Google Search Console. They are;
- Overview
- Performance
- Coverage
- Sitemaps
- Enhancements
- Mobile usability
- Sitelinks searchbox
- Security and manual actions
- Links
- Settings
Let’s go through each of these in more detail.
Overview
The overview screen is what you see when you first log in. It shows the property you are viewing, and then three panels; performance, coverage and enhancements.
Performance graph
This is a quick view of how your website is performing in search results. You can click Open report to get further detail.
Coverage graph
This is a quick view to how your website is being indexed by Google. You can click Open report to get further detail.
The graph will display valid pages (in green) and pages with errors (in red). It may also show Google Search Updates as a small dot below a specific date, which you can click on to read more information.
In this example above, there were 401 pages indexed by Google (the green line), and zero pages with errors (the red line).
Enhancements panel
This panel shows data for any website enhancements you have. For most website owners, it will display mobile usability and (if relevant) sitelinks searchbox.
Others may show logo, AMP, rich results and more, depending on what enhancements you have.
Performance
This is one of the most interesting datasets that search console can display.
It reveals interesting data, such as;
- Total clicks
- Total impressions
- Average CTR
- Average Position
In this example, you can see that pages within this website were displayed in Google search results a whopping 12.9 million times in the last three months.
As a result, 558,000 clicks occurred, meaning they became visitors to the website.
You can also see the average CTR, click through rate, which means what percentage of users clicked on a search result to your website after viewing it. In the above example it was 4.3%, which means for each 100 people who saw your website in search results, 4.3 of them clicked on it.
You want to do your best to optimise your search result click through rates – the higher you can get that Average CTR, the more traffic you will likely be receiving.
This all boils down to how you structure your website code, and if you use META description, OG tags and the like.
Finally, the Average position tells you where your pages sit within search results. This example shows 17.4, which is what we would say as ‘second page’.
Improving your click through rates (CTR) from Google search results
It doesn’t matter how great your website content is – if people see the results in Google, and aren’t encouraged by what they see, they will not click.
Let’s say I want to find Tesla car dealerships in Australia. I search Google for ‘tesla dealers australia’
The first result shows that that page has actual contact data for various dealerships, as I can see in the four lines of content (the grey text) under the page title (the blue and larger text).
The second results shows two lines of content under the page title, which starts with a list of available website languages.
Now, which one are you likely to click on?
To avoid having landing pages like the latter appearing in Google search results for your own website, you need to focus on three things;
Page title
This appears in larger text in search results. Every page of your website should have a descriptive title, which is unique from every other page on your website. When I say descriptive, avoid titles like ‘Home’ or ‘Services’. A better version of ‘Services’ would be “We provide a wide range of widget polishing services at Widget Co.”
The more enticing and descriptive, the better the chance a searcher will click on your page. Your page tiles should be around 50-60 characters long.
Meta description
Google sometimes (not always) uses your page’s meta description. This should be also entirely unique for each page. A meta description looks like the following;
<meta name="description" content="We provide a full range of family law services throughout Western Australia, including Perth, Fremantle, Albany and Broome. "/>
You should try to keep your meta description length to around 120 characters long.
Page content
Finally, Google sometimes uses actual relevant page content instead of meta descriptions. In the previous Tesla example, neither page had a meta description, so Google choose related content to display in the results.
You want to ensure that your website pages are unique, and relevant to that specific page. It’s pointless talking about Tesla vehicles on your family law website, as an example.
Coverage
The coverage screen within the Google Search Console shows more detail about individual pages within your website, and if Google had any trouble crawling them for inclusion in their database.
In an example, 401 pages were included, and 1.88 thousand were excluded. This was intentional, and is driven by the robots.txt file and settings on the website itself.
Importantly, this screen shows there were no errors at all, and no warnings, which is perfect.
If there were errors, it would look more like the following example screen. This screen shows there were 23 pages that had errors.
This was likely URL’s submitted via the sitemap, automatically.
Of these 23, 17 showed to Google as 404 not found, and 6 were what Google calls ‘Soft 404’pages, which could be the result of a few different scenarios, such as a page with very little to no content at all, or a page that is blank, yet showing a 200 response, which means ‘Found’.
You can read more about Soft 404 errors, here.
Sitemaps
In an ideal situation, Google is looking for you to submit a website sitemap, which is a small file that outlines all the pages and URL’s on your website. There is a standard for these files, called the ‘standard sitemap protocol’.
Google accepts sitemaps in XML, text, RSS and Atom formats.
Most content management systems have a way of doing these automatically, either built into the CMS, or available as a module or plugin.
If you have a sitemap available, it is important to submit that in the sitemap screen, which will allow Google to track this sitemap, and be alerted when there are additions or changes at all.
Enhancements
This screen shows you all the enhancements your website has, such as mobile usability, sitelinks searchbox, logo and similar.
Enhancements are used by Google to create what we call ‘rich results’ in their search results.
These are enhancements that those two website owners have created within their website, using structured data.
You can prepare your website with these enhancements, however Google clearly states they may not use them anyway. This is because these enhancements depend on a number of factors that Google takes into account, such as location, search device type, site speed, and most importantly whether Google thinks the feature would provide the best search experience for the user.
When there is a reported enhancement, Google will show both an overview, as well as a specific screen for each enhancement.
There are many enhancements available to websites, all of which are typically controlled by using structured data.
Enhancements can include;
- Website logo
- Contact details
- Job postings
- Recipes
- Book reviews
- Critic reviews
- Image carousel
- Product data
- And many more.
The best way to get started with including structured data within your website, is to read up on this very handy guide thanks to Google, Understand how structured data works.
Security and manual actions
Google Search Console also has a few screens for more manual actions, driven by the website owner. These are ‘Links’ and ‘Settings’.
Links
The links screen shows all the external websites pointing to your website, as well as all links within your website, pointing to other pages (called internal links)
Given the importance of backlinks in search engine rankings, this screen is a goldmine of information for a website owner.
Clicking on the More link on any of these panels will reveal further information, such as how many links are coming from each external website.
Settings
The settings screen shows a few important elements;
If you are the verified owner of the website or not. If it shows you aren’t, follow the instructions at the top of this article to get verified.
Who has access to the search console, and what permissions they have, within it. The ability to add your digital marketing agency or web designer to search console access if valuable, and allows us (or them) to have access to your data as well.
What indexing crawler is Google using for your website.
This is important. Google swapped to mobile-first indexing as the default from 1st July 2019. For existing websites prior to this date, many have already been swapped to mobile first, depending on their code.
As Google states “we continue to monitor and evaluate pages based on the best practices. We notify site owners through Search Console once they're seen as being ready. Since the default state for new sites is mobile-first indexing, there's no need to send a notification to new sites.”
How to disavow links
When looking in the links screens, you may find unsavoury or low value inbound links that may actually be harming your rankings in Google.
What you need to do, is tell Google that you don’t want these links pointing at your website, and ideally Google should just ignore them.
That’s why the Disavow links tool is of value. You can inform Google of the links you want it to ignore, by providing a file.
The easiest method to do this, is to download the ‘Top linking sites’ CSV file by clicking on the down arrow at the top right of this panel.
Now open the file in excel or Google Sheets to see the list of domains.
You have the choice when disavowing links, to either block all links from a website, or by blocking specific pages that have the links.
The former is easier, however if the domain has a mix of good and bad links, you’ll want to do specific pages.
Let’s go step by step through the process.
Start by copying the first column into a new text file.
Then, remove all the domains you have good inbound links coming from.
This should leave you with the domains with bad links,
Blocking whole domains
Let’s say you want to block all links coming from the website at anotherdomain.net in the above example.
To do this, you want to add domain: at the start of this line.
domain:anotherdomain.net
Blocking specific pages
Let’s say thisdomain.com.au has 3 links pointing to you, one of which is low value, and you want to disavow just that one.
You know the full URL of the page this link appears, so you can change the line with that domain to the full URL, such as;
http://www.thisdomain.com.au/s... you will have a text file that looks like;
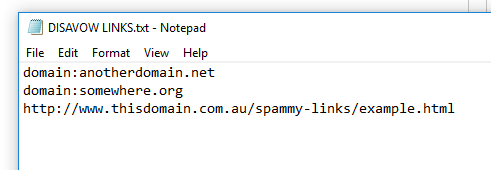
Disavow links instructions
Now that you have done this, and ensured you save the file as a text file, with the extension txt, you are ready to upload the file.
A warning though – if you have ever uploaded a disavow links file before, this new one will overwrite the old one. You’ll want to ensure you have blocked all the low quality links from the last file in this file as well.
When you’re ready, head over to the Disavow links tool. Choose the right website (if you have more than one website associated with your Google Search Console account), and then click the ‘Disavow Links’ button.
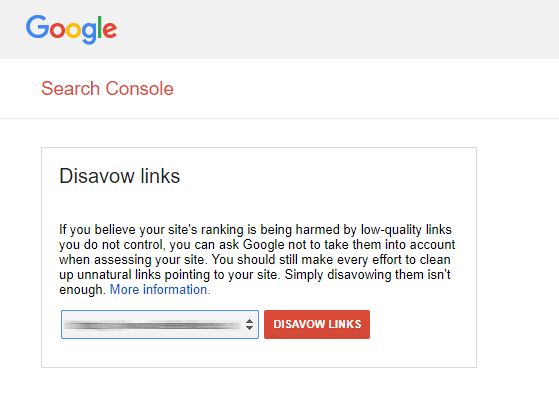
Google disavow links tool
When you have chosen the correct website, and clicked next, you will be prompted to upload your newly completed text file.
Now upload the text file.
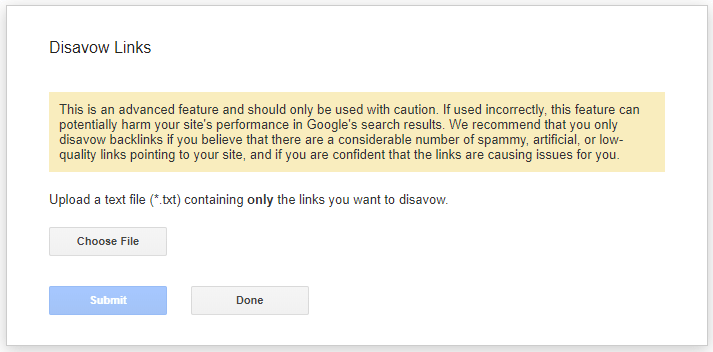
Google disavow links process
Once this has been done, it may take up to 3-4 weeks for Google to recognise the instructions. Don’t panic if they’re still there the next day – eventually they will disappear off your Google Search Console, which means that Google has now ignored those links.
Google Search Console: Summary
There you have it, the Australian website owners guide to Google Search Console. If you haven’t already, I recommend you sign up to Google Search Console, and submit your verification and add a website sitemap.
Once your Google Search Console data has populated, here are the five key tasks you should continue to monitor and improve;
1. Look for sitemap errors and fix them.
2. You should keep an eye on any website errors, and fix them promptly.
3. Experiment with various ways to improve your click through rates.
4. Keep your eye on inbound links, and look for spammy or low quality links that you should disavow.
5. Finally, do your best to add search enhancements, which will increase the chance that people searching Google will click through to your website.
All the best of luck!
